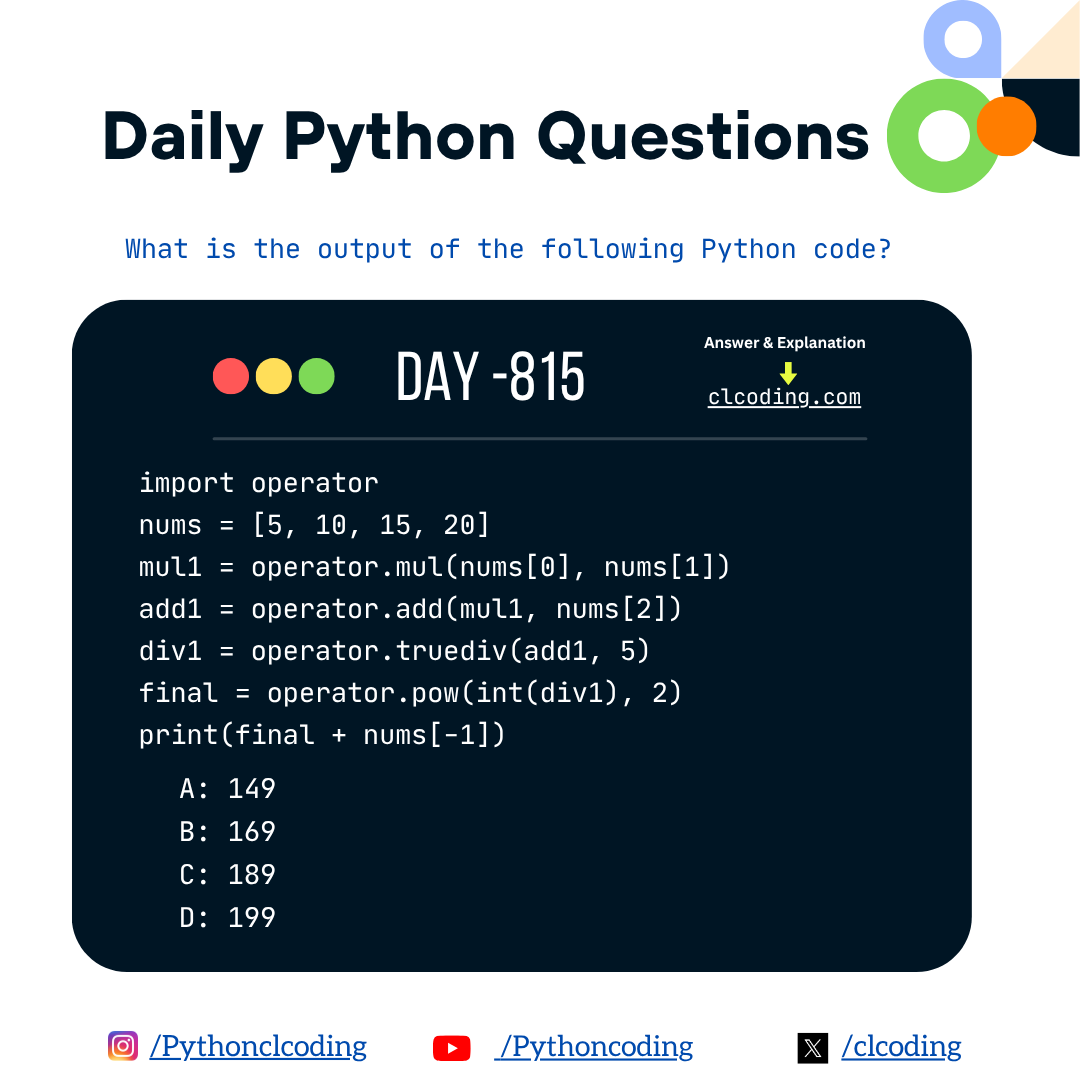
Code Explanation:
Importing the Operator Module
import operator
This imports Python’s built-in operator module, which contains function versions of basic arithmetic operations like add, mul, pow, truediv, etc.
Instead of using symbols like +, *, /, you can use these function forms — for example, operator.add(2,3) does the same as 2 + 3.
Creating a List of Numbers
nums = [5, 10, 15, 20]
This creates a list named nums containing four integers:
[5, 10, 15, 20]
You’ll use these numbers in various arithmetic operations below.
Multiplying the First Two Numbers
mul1 = operator.mul(nums[0], nums[1])
nums[0] is 5
nums[1] is 10
operator.mul(5, 10) multiplies them.
So mul1 = 50.
Adding the Third Number
add1 = operator.add(mul1, nums[2])
mul1 is 50
nums[2] is 15
operator.add(50, 15) adds them together.
So add1 = 65.
Dividing the Sum by 5
div1 = operator.truediv(add1, 5)
add1 is 65
Divide by 5 → operator.truediv(65, 5) = 13.0
So div1 = 13.0.
Squaring the Integer Part
final = operator.pow(int(div1), 2)
int(div1) converts 13.0 to 13
operator.pow(13, 2) means
So final = 169.
Adding the Last Element of the List
print(final + nums[-1])
nums[-1] means the last element of the list, which is 20
Adds final + 20 → 169 + 20 = 189
So the final value printed is 189.
Output
189

.png)





.png)









.png)

























0 Comments:
Post a Comment