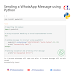
a. range(5)
b. range(1, 10, 3)
c. range(10, 1, -2)
d. range(1, 5)
e. range(-2)
Let's break down each of the provided ranges:
a. range(5) - This generates a sequence of integers from 0 to 4 (5 is the stopping value, exclusive). So, it produces the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4.
b. range(1, 10, 3) - This generates a sequence of integers starting from 1, up to, but not including 10, with a step of 3. So, it produces the numbers 1, 4, 7.
c. range(10, 1, -2) - This generates a sequence of integers starting from 10, down to, but not including 1, with a step of -2. So, it produces the numbers 10, 8, 6, 4, 2.
d. range(1, 5) - This generates a sequence of integers starting from 1, up to, but not including 5. So, it produces the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4.
e. range(-2) - This is a bit different. range() requires at least two arguments (start, stop), but here you've provided only one. If you want to generate a range starting from 0 up to, but not including -2, you would need to provide the start and stop values. If you intended to start from 0 and go up to -2, you could use range(0, -2), which would produce the numbers 0, -1.
So, to summarize:
a. 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
b. 1, 4, 7
c. 10, 8, 6, 4, 2
d. 1, 2, 3, 4
e. (Assuming you meant range(0, -2)) 0, -1


.png)
.png)













.png)


















.png)