Thursday, 23 October 2025
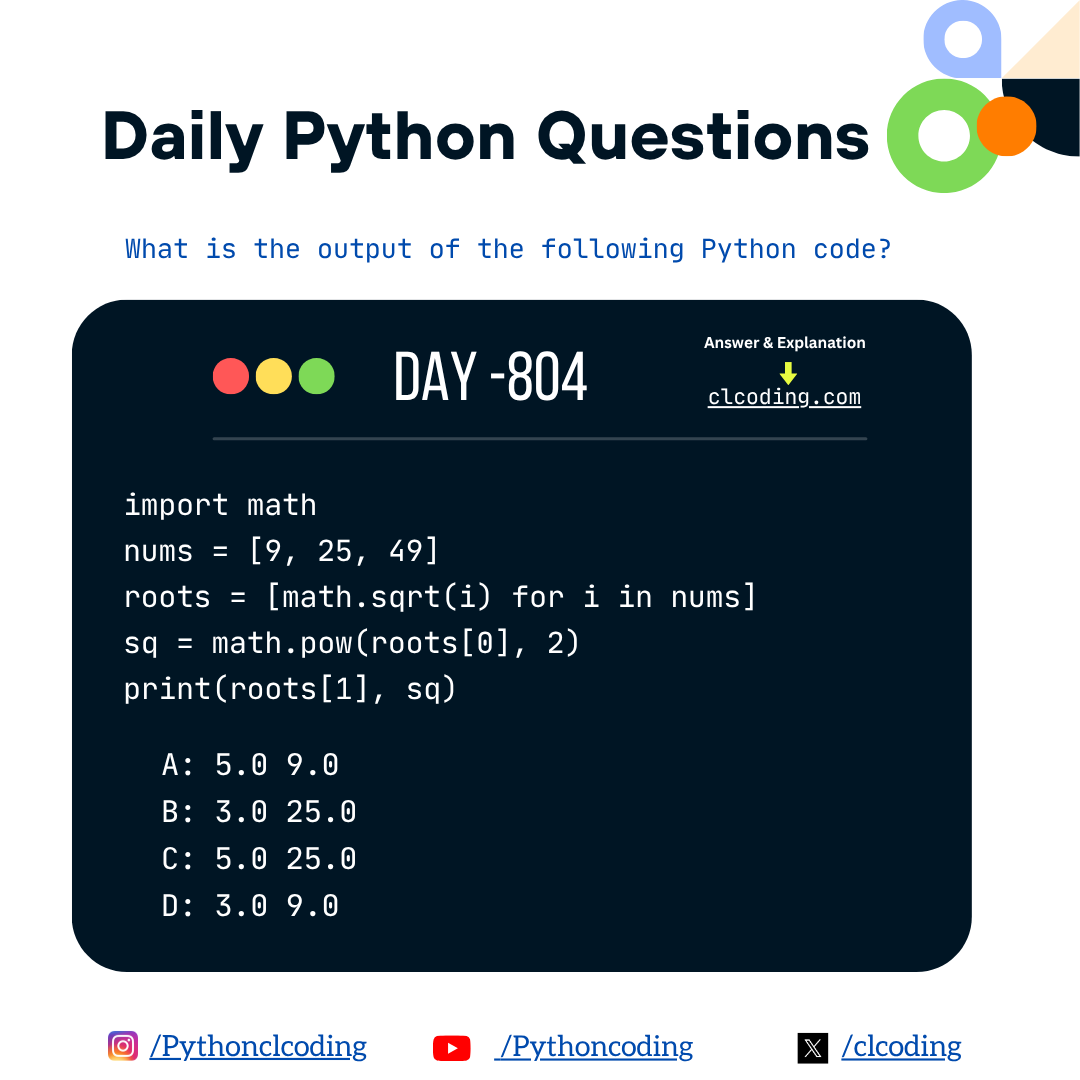
Python Coding challenge - Day 804| What is the output of the following Python Code?
Python Developer October 23, 2025 Python Coding Challenge No comments
Code Explanation:
Final Output
Wednesday, 22 October 2025
ChatGPT Atlas: The Future of Intelligent Browsing vs Comet and Chrome
Python Coding October 22, 2025 AI No comments
🚀 Why ChatGPT Atlas Is Better Than Comet and Chrome
In the rapidly evolving world of AI and browsers, ChatGPT Atlas has emerged as a true game-changer. While tools like Comet and Google Chrome have their own strengths, ChatGPT Atlas redefines how we interact with the web, learn, and work — all within a single intelligent environment.
Let’s dive into why ChatGPT Atlas outshines both Comet and Chrome in functionality, innovation, and productivity.
🧠 1. AI + Browser = The Ultimate Fusion
Unlike Chrome, which simply displays web pages, or Comet, which focuses on AI benchmarking and testing, ChatGPT Atlas combines AI intelligence with real-time web access.
You can browse websites, summarize content, write code, and even generate creative ideas — all powered by GPT-5 intelligence. It’s not just browsing; it’s understanding the web.
⚡ 2. All-in-One Workspace for Everything
With ChatGPT Atlas, you don’t need multiple apps. You can:
-
Browse the web intelligently
-
Generate Python code
-
Analyze data
-
Create blog posts, visuals, or reports
-
Manage projects and notes
It’s a complete productivity ecosystem, unlike Chrome, which depends heavily on extensions, or Comet, which serves a narrow technical purpose.
💬 3. Smarter Interaction, Personalized Experience
ChatGPT Atlas doesn’t just follow commands — it understands your intent.
It remembers your context, past conversations, and preferences to deliver more personalized and continuous support, while Chrome and Comet reset your session each time.
🔍 4. Live Web + Reasoning Power
Chrome shows you web pages; ChatGPT Atlas thinks with you.
You can ask Atlas to:
-
Summarize a webpage
-
Compare tools
-
Write an analysis
No copy-paste, no switching between tabs — Atlas integrates AI reasoning directly into browsing.
🧩 5. Perfect for Developers, Creators & Learners
Whether you’re a developer debugging code, a student learning new concepts, or a creator writing blogs, ChatGPT Atlas adapts to your workflow.
It supports real-time coding, documentation, visualization, and research — something neither Comet nor Chrome offers natively.
🌟 Final Thoughts
ChatGPT Atlas isn’t just an upgrade — it’s the next generation of browsers.
By merging intelligence, context, and creativity, it empowers users to do everything faster, smarter, and better.
If Chrome is the window to the web, ChatGPT Atlas is the bridge between the web and your mind.
Master Machine Learning with TensorFlow: Basics to Advanced
Python Developer October 22, 2025 Machine Learning No comments
Master Machine Learning with TensorFlow: Basics to Advanced – A Comprehensive Guide
The "Master Machine Learning with TensorFlow: Basics to Advanced" course on Coursera is a meticulously designed program aimed at equipping learners with both foundational and advanced skills in machine learning (ML) using Python and TensorFlow. This course provides a hands-on, project-based learning experience, making it suitable for both beginners and those looking to deepen their understanding of ML concepts.
Course Overview
This intermediate-level course spans approximately two weeks, with an estimated commitment of 10 hours per week. It is divided into five comprehensive modules, each focusing on different aspects of machine learning and TensorFlow. The course emphasizes practical applications, ensuring that learners can apply the concepts to real-world problems.
Module Breakdown
Module 1: Getting Started with Machine Learning
This introductory module sets the stage by explaining the fundamentals of machine learning, its real-world applications, and the tools required for hands-on practice. Learners are introduced to the concept of machine learning, understanding how machines learn and where ML is applied across various industries. The module also covers the setup of the programming environment, including the installation and usage of Jupyter Notebooks.
Module 2: Tools of the Trade – Jupyter, Anaconda & Libraries
In this module, learners delve into essential tools for machine learning. They gain proficiency in using Anaconda for environment management, Jupyter Notebooks for interactive coding, and Python libraries such as NumPy and Pandas for data manipulation. The module also introduces data visualization techniques using Matplotlib and Seaborn, enabling learners to effectively analyze and interpret data.
Module 3: Data Analysis & Visualization
Building upon the previous module, this section focuses on data analysis and visualization. Learners explore various data preprocessing techniques, including handling missing values, encoding categorical variables, and scaling features. They also learn to visualize data distributions and relationships, which are crucial for understanding the underlying patterns in the data.
Module 4: Classical Machine Learning Algorithms
This module introduces learners to classical machine learning algorithms. Learners implement and evaluate algorithms such as linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees, and support vector machines. The module emphasizes model evaluation metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, providing learners with the tools to assess model performance effectively.
Module 5: Deep Learning with TensorFlow
The final module transitions into deep learning, focusing on building and training neural networks using TensorFlow. Learners understand the architecture of neural networks, including layers, activation functions, and optimization techniques. The module culminates in a project where learners apply their knowledge to solve a real-world problem, reinforcing the concepts learned throughout the course.
Skills Acquired
Upon completing this course, learners will have developed proficiency in:
-
Setting up and managing ML environments using Anaconda and Jupyter Notebooks
-
Utilizing Python libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, and Seaborn for data manipulation and visualization
-
Implementing classical machine learning algorithms and evaluating their performance
-
Building and training neural networks using TensorFlow
-
Applying machine learning techniques to real-world problems
Career Impact
Completing this course prepares learners for various roles in the field of machine learning and artificial intelligence, including:
-
Machine Learning Engineer
-
Data Scientist
-
AI Research Scientist
-
Software Developer specializing in AI
The practical skills acquired through this course are highly valued in industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, and e-commerce.
Join Now: Master Machine Learning with TensorFlow: Basics to Advanced
Final Thoughts
The "Master Machine Learning with TensorFlow: Basics to Advanced" course offers a comprehensive pathway for learners to acquire both foundational and advanced skills in machine learning. Through a structured curriculum and hands-on projects, learners gain practical experience that is directly applicable to real-world scenarios. Whether you are a beginner exploring machine learning or a professional looking to enhance your skills, this course provides the knowledge and tools necessary to succeed in the field of machine learning.
AI Deep Learning in Image Processing
Python Developer October 22, 2025 AI, Deep Learning No comments
Introduction to AI and Deep Learning in Image Processing
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Deep Learning (DL) have revolutionized the field of image processing, enabling machines to perform tasks that were once considered exclusive to human vision. Traditional image processing techniques often relied on manual feature extraction and rule-based algorithms. In contrast, AI and DL methods, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), learn hierarchical features directly from raw image data, leading to significant improvements in accuracy and efficiency.
Key Concepts and Techniques
1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
CNNs are the cornerstone of modern image processing. They consist of layers that automatically detect features such as edges, textures, and patterns, which are crucial for tasks like object recognition and classification.
2. Image Classification
This involves categorizing images into predefined classes. DL models, trained on large datasets, can achieve human-level performance in classifying images across various domains, including medical imaging, satellite imagery, and facial recognition.
3. Object Detection and Localization
Beyond classification, AI models can identify and locate objects within an image. Techniques like Region-based CNNs (R-CNNs) and You Only Look Once (YOLO) have been developed to perform real-time object detection, which is vital for applications like autonomous driving and surveillance systems.
4. Image Segmentation
Segmentation divides an image into meaningful parts, facilitating tasks such as medical image analysis and scene understanding. Fully Convolutional Networks (FCNs) and U-Net architectures are commonly used for pixel-wise segmentation.
5. Generative Models
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are employed to generate new images or modify existing ones. These models are used in applications ranging from image super-resolution to artistic style transfer.
Applications in Various Domains
-
Medical Imaging: AI models assist in diagnosing diseases by analyzing X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, often detecting abnormalities that may be missed by human clinicians.
-
Agriculture: DL techniques are applied to monitor crop health, detect pests, and estimate yields through aerial imagery.
-
Security and Surveillance: AI-powered systems can identify individuals, detect unusual activities, and enhance video feeds in real-time.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Image processing enables vehicles to interpret their surroundings, recognize traffic signs, and navigate safely.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the advancements, several challenges remain:
-
Data Annotation: Obtaining labeled datasets for training models can be time-consuming and expensive.
-
Computational Resources: Training deep learning models requires significant computational power, often necessitating specialized hardware like GPUs.
-
Interpretability: Understanding the decision-making process of AI models is crucial, especially in critical applications like healthcare.
Future research is likely to focus on developing more efficient algorithms, improving model interpretability, and addressing ethical considerations in AI deployment.
Hard Copy: AI Deep Learning in Image Processing
Kindle: AI Deep Learning in Image Processing
Conclusion
AI and deep learning have transformed image processing, enabling machines to perform complex visual tasks with remarkable accuracy. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of AI in image processing is expected to expand, offering innovative solutions across various industries.
The Most Complete AI Agentic Engineering System: Step-by-step guide to build, optimize, and scale LLM agents—with exclusive monthly and rigorous ... metrics, and built-in self-improvement
Introduction
In 2025 the field of AI is rapidly shifting beyond static models to agentic systems—multi-step, autonomous agents built around large language models (LLMs) that can plan, reason, execute actions and improve themselves over time. The book The Most Complete AI Agentic Engineering System aims to capture this evolution. From building an initial prototype to optimizing, scaling, benchmarking and even self-improvement, it offers a full roadmap for creating real-world agent-driven applications.
Why This Book Matters
Most AI books focus on single models or narrow tasks (e.g., a chatbot or a prediction model). This book takes a broader view: it treats the agentic architecture as the unit of work. In other words, you’re not just building an LLM or a classifier; you’re building a software system of interacting agents, feedback loops, performance metrics and deployment infrastructure. If you’re serious about moving into advanced AI workflows—LLM orchestration, agent frameworks, continuous improvement—this book is positioned to deliver practical guidance.
What You Will Learn
Building the Agent Structure
The book begins with setting up an agentic environment: defining goals, selecting LLMs or tools, designing agent workflows (planning + action loops), and integrating tools/APIs. Readers learn how to architect systems where an agent monitors a task, breaks it down into subtasks, assigns them (perhaps to other agents), and iterates until completion.
Optimizing and Benchmarking
Once an agent is built, the next challenge is measuring and improving its performance. This book emphasizes rigorous benchmarking frameworks, custom metrics, monthly assessment protocols and continuous improvement cycles. You learn how to define KPIs, track agent behaviour over time, analyze failures/hallucinations, and refine prompts, tool usage and workflows accordingly.
Scaling Agentic Systems
A small-scale agent prototype is one thing; scaling to production with many agents, parallel workflows, tool integrations and monitoring is another. This book addresses deployment architectures, orchestration of agents, resource management (compute, APIs), logging/tracing, and governance. It gives guidance on going from prototype to enterprise-grade agentic systems.
Self-Improvement and Feedback Loops
A standout feature is the built-in self-improvement model: how to build agents that learn from their own performance, adapt workflows, log mistakes, and refine their logic. The book shows how to embed self-evaluation loops, human-in-the-loop feedback, automated retraining and knowledge accumulation so your system gets better instead of stagnating.
Who Should Read It
This book is ideal for developers, AI engineers, system architects and data scientists who want to move beyond single-model experiments to end-to-end agentic systems. If you have background in LLMs, tool integration (e.g., LangChain, AutoGen, AgentGPT), and are ready to build scalable workflows, this book will give you structure and best practices. If you’re a beginner or only familiar with basic ML or chatbots, you may find some sections advanced, but still valuable as a forward-looking resource.
Key Benefits
-
A roadmap for building agentic systems rather than just models
-
Detailed guidance on metrics, evaluation frameworks and continuous improvement
-
Coverage of production-scale concerns: deployment, orchestration, monitoring
-
Emphasis on self-improving agents with feedback loops — a modern frontier in AI
-
Practical focus with step-by-step instructions, design patterns and workflows
A Few Considerations
-
Because the field of agentic AI is rapidly evolving, some tools, frameworks or best practices may change quickly. Use this book as a strong foundation, but stay ready to adapt to new libraries and technologies.
-
Designing agentic systems raises non-trivial governance, safety, bias, and oversight issues. While the book covers measurement and feedback loops, readers should also consider ethical and regulatory dimensions.
-
Building full-scale agentic systems can be resource-intensive (compute, API calls, monitoring infrastructure). Be prepared for practical constraints when scaling beyond prototypes.
Hard Copy: The Most Complete AI Agentic Engineering System: Step-by-step guide to build, optimize, and scale LLM agents—with exclusive monthly and rigorous ... metrics, and built-in self-improvement
Kindle: The Most Complete AI Agentic Engineering System: Step-by-step guide to build, optimize, and scale LLM agents—with exclusive monthly and rigorous ... metrics, and built-in self-improvement
Final Thoughts
If you’re ready to go beyond building isolated AI models and want to architect systems of autonomous agents that scale, adapt, and improve over time, then The Most Complete AI Agentic Engineering System is a compelling read. It offers a modern blueprint for the next wave of AI applications—agentic systems powered by LLMs, design patterns, metrics and production workflows. If your goal is to build real-world AI products or services that go well beyond what traditional ML offers, this book deserves a place on your shelf.
Machine Learning: Python for Data Science: A Practical Guide to Building, Training, Testing and Deploying Machine Learning / AI models
Python Developer October 22, 2025 AI, Data Science, Machine Learning No comments
Machine Learning with Python: A Practical Guide for Real-World AI
Introduction
Machine learning has rapidly evolved from a niche academic field into a core technology that powers modern industries. From recommendation systems and fraud detection to healthcare diagnostics and autonomous systems, machine learning is now central to innovation. However, while many learners focus on algorithms and theory, far fewer understand how to apply machine learning in real projects. The book Machine Learning: Python for Data Science – A Practical Guide to Building, Training, Testing and Deploying Machine Learning / AI Models addresses this gap by offering readers a complete, hands-on approach to building machine learning solutions end to end.
A Practical, End-to-End Approach
One of the strongest aspects of this book is its focus on the full machine learning lifecycle. Real-world machine learning is not just about building a model. It involves preparing data, testing models, tuning performance, deploying solutions, and ensuring they continue to work in real environments. This book guides the reader through each step in a structured and practical manner, using Python as the primary language.
Learning to Work with Data
The journey begins with understanding and preparing data. The book teaches how to work with libraries such as Pandas and NumPy to load, clean, analyze, and transform data. Since real-world data is often incomplete, noisy, or inconsistent, this section helps readers develop the skills to make datasets usable and ready for modeling.
Building and Training Machine Learning Models
After mastering data preparation, the book moves into building models using Python’s machine learning libraries, especially scikit-learn. Readers are introduced to key machine learning tasks such as classification, regression, and clustering. The material covers how different algorithms work, why to choose one over another, and how to interpret their outcomes. By following the guided examples, readers learn not only to train models, but also to think like machine learning practitioners.
Model Testing and Evaluation
A model is only useful if it performs well, and the book clearly explains how to evaluate performance. It covers essential techniques such as train-test splits, cross-validation, and model comparison. The book also explains performance metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and error rates, helping readers understand how to diagnose problems such as overfitting and underfitting. This is crucial for building models that are both accurate and reliable.
Deploying Machine Learning Models
One of the most valuable parts of the book is its coverage of deployment. Many resources stop after model training, but in real environments, a model must be integrated into applications and made accessible to users. The book explains how to save and export models, serve them through APIs, and deploy them into systems or cloud platforms. This transforms a local experiment into a working AI solution that can be used in real time.
Who Will Benefit From This Book
This book is especially useful for aspiring data scientists, Python developers, and students who want practical skills rather than just theoretical knowledge. It is also beneficial for software engineers who wish to incorporate machine learning into real-world systems. Since the content progresses step by step, readers with basic Python understanding can follow along and grow into confident practitioners.
Hard Copy: Machine Learning: Python for Data Science: A Practical Guide to Building, Training, Testing and Deploying Machine Learning / AI models
Conclusion
Machine Learning: Python for Data Science provides a complete and practical roadmap for anyone looking to master machine learning from the ground up. By focusing on real-world workflows and hands-on implementation with Python, it prepares readers to build, test, and deploy machine learning models with confidence. For learners who want to move beyond theory and start creating impactful AI solutions, this book is a strong and valuable resource.
Python Coding Challange - Question with Answer (01221025)
Python Coding October 22, 2025 Python Quiz No comments
Step-by-step explanation:
-
Initialization
x = 'abcd'Here, the variable x is assigned the string 'abcd'.
-
Loop setup
for i in range(len(x)):len(x) = 4
-
So, range(len(x)) = range(4) → iterates through 0, 1, 2, 3.
-
Inside the loop
x = 'a'-
On the first iteration (i = 0), x becomes 'a'.
-
On the next iterations, range(len(x)) was already evaluated as range(4) before the loop began — so it will still run 4 times, even though x changed inside.
-
Each time, x is reassigned to 'a' again (no change after the first time).
-
-
After the loop
print(x)-
The final value of x is 'a'.
-
✅ Output:
aKey concept:
range(len(x)) is evaluated once at the start of the loop.
-
Changing x inside the loop doesn’t affect how many times the loop runs.
-
The loop overwrites x repeatedly, so only the last assignment ('a') remains.
Decode the Data: A Teen’s Guide to Data Science with Python
Natural Language Processing with Classification and Vector Spaces
Python Developer October 22, 2025 AI, Machine Learning No comments
Natural Language Processing with Classification and Vector Spaces
Introduction
In an era where digital communication dominates, understanding and processing human language has become a core skill in artificial intelligence. From chatbots to translation systems and sentiment analysis tools, Natural Language Processing (NLP) powers much of our modern AI landscape.
The Natural Language Processing with Classification and Vector Spaces course, created by DeepLearning.AI on Coursera, introduces learners to the fundamental techniques that make NLP systems work — classification models and vector space representations.
Why This Course Matters
Every day, billions of text-based interactions occur — tweets, emails, reviews, and articles. The ability to automatically understand and categorize this text data gives businesses and researchers powerful insights. Traditional rule-based systems fall short when handling ambiguity, context, or slang.
This course teaches how AI overcomes these challenges through classification algorithms and vector space models. Classification helps categorize text (e.g., positive vs. negative sentiment), while vector spaces represent the meaning of words as numerical values, allowing computers to measure similarity, context, and relationships between words.
By combining these techniques, learners gain a deep understanding of how machines learn to read and interpret human language.
Course Overview
The course is an intermediate-level program designed for learners with a background in programming and basic machine learning. It’s the first course in the Natural Language Processing Specialization by DeepLearning.AI and provides a hands-on introduction to NLP’s core building blocks.
Through four well-structured modules, the course guides students from simple text classification to advanced vector representations and practical applications like translation and document search.
Module 1 — Sentiment Analysis with Logistic Regression
The course begins with one of the most common NLP applications — sentiment analysis. Learners start by converting text into numeric features using techniques like the bag-of-words model. Then, they train a logistic regression classifier to distinguish between positive and negative sentiments in text data.
This module provides a solid foundation in preprocessing, feature extraction, and model evaluation — key steps in any NLP workflow.
Module 2 — Sentiment Analysis with Naïve Bayes
Next, the course introduces the Naïve Bayes classifier, a probabilistic model widely used in text analysis. Learners explore how Bayes’ Theorem underpins this model and apply it to classify sentences or tweets based on sentiment.
This module highlights the differences between logistic regression and Naïve Bayes, helping students understand the strengths, assumptions, and limitations of each approach in real-world scenarios.
Module 3 — Vector Space Models
This module shifts focus from classification to representation learning — understanding how words can be embedded into mathematical space. Learners explore word embeddings, where each word is represented as a dense vector that captures its semantic meaning.
By examining geometric relationships in these vector spaces, students can perform tasks like finding word similarities and analogies (e.g., “king – man + woman = queen”).
Concepts like cosine similarity, Euclidean distance, and dimensionality reduction (PCA) are covered, allowing learners to visualize and interpret how language relationships emerge from data.
Module 4 — Machine Translation and Document Search
The final module demonstrates how these embeddings can be applied to complex NLP tasks such as word translation and document search. Learners use pre-trained word vectors to translate words between languages or find semantically related documents.
This section ties together all previous concepts, showing how vector representations enable scalable and intelligent text-processing systems that go beyond simple keyword matching.
Who Should Take This Course
This course is ideal for:
-
Machine learning enthusiasts looking to enter the NLP field.
-
Data scientists and engineers who want to apply ML techniques to text data.
-
Developers seeking to build chatbots, recommendation systems, or search engines.
-
Researchers and students eager to understand the foundations of language modeling.
A basic understanding of Python and fundamental ML concepts will help learners get the most out of the course.
Skills You’ll Gain
By the end of the course, you’ll have mastered:
-
Text preprocessing and feature extraction techniques.
-
Logistic regression and Naïve Bayes classifiers for text analysis.
-
Word embeddings and semantic vector representations.
-
Similarity metrics and analogy reasoning in vector spaces.
-
Practical applications like translation and document retrieval.
These skills form the foundation of modern NLP and open doors to advanced topics like deep learning, transformers, and generative language models.
Learning Tips
To make the most of the course:
-
Engage with the programming assignments — they bring the theory to life.
-
Experiment with your own datasets to apply the learned techniques to real-world problems.
-
Visualize word embeddings to understand how semantics emerge from data.
-
Compare classifiers — try both logistic regression and Naïve Bayes on the same dataset to see differences in performance.
-
Build a mini-project — such as sentiment analysis on movie reviews or social media posts — to reinforce your understanding.
Career Impact
NLP is one of the most in-demand domains in AI. Companies across industries — from healthcare to finance — are investing in tools that can analyze language data for insights.
This course equips learners with the practical and theoretical foundation to pursue roles such as:
-
NLP Engineer
-
Machine Learning Specialist
-
Data Scientist
-
AI Research Assistant
The certification from DeepLearning.AI also adds strong credibility to your profile and demonstrates that you understand the essential mechanics of NLP.
Join Free: Natural Language Processing with Classification and Vector Spaces
Conclusion
Natural Language Processing with Classification and Vector Spaces is a must-take course for anyone looking to understand how machines interpret human language. By combining theory, coding exercises, and real-world applications, it bridges the gap between linguistic concepts and practical AI systems.
Whether you’re aiming to build smarter chatbots, design recommendation engines, or simply understand how words can be transformed into meaningful mathematical forms, this course offers a solid foundation to start your NLP journey.
Tuesday, 21 October 2025
Python Coding challenge - Day 801| What is the output of the following Python Code?
Python Developer October 21, 2025 Python Coding Challenge No comments
Code Explanatiion:
Python Coding challenge - Day 799| What is the output of the following Python Code?
Python Developer October 21, 2025 Python Coding Challenge No comments
Code Explanation:
Output:
Python Coding challenge - Day 798| What is the output of the following Python Code?
Python Developer October 21, 2025 Python Coding Challenge No comments
Code Explanation:
Output you get:
Python Coding challenge - Day 800| What is the output of the following Python Code?
Python Developer October 21, 2025 Python Coding Challenge No comments
Code Expplanation:
Final Output
Python Coding Challange - Question with Answer (01211025)
Python Coding October 21, 2025 Python Quiz No comments
Step-by-Step Execution:
-
Initialization:
i = 0The variable i starts with value 0.
-
First iteration:
-
Condition i < 3 → 0 < 3 ✅ True
-
Check if i == 1 → 0 == 1 ❌ False
-
Execute print(i) → prints 0
-
Execute i += 1 → now i = 1
-
-
Second iteration:
-
Condition i < 3 → 1 < 3 ✅ True
-
Check if i == 1 → 1 == 1 ✅ True
break is executed → loop immediately stops
-
-
Else block:
else:
print("Done")The else part of a while loop runs only if the loop finishes normally
— that is, without encountering a break.But since a break was used, the else block is skipped.
Final Output:
0
Key Concept:
In Python, a while loop’s else executes only when the loop ends naturally (i.e., the condition becomes false).
If the loop ends because of a break, the else part is not executed.
APPLICATION OF PYTHON FOR CYBERSECURITY
Monday, 20 October 2025
AI for Cybersecurity
Python Developer October 20, 2025 AI, Cybersecurity No comments
AI for Cybersecurity — The Future of Digital Defense
Introduction
In today’s hyperconnected world, cyber threats are evolving faster than ever. Traditional defense mechanisms like firewalls and signature-based detection are no longer enough. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) steps in, offering a smarter, adaptive approach to cybersecurity. The AI for Cybersecurity course on Coursera provides an in-depth exploration of how AI and Machine Learning (ML) can be applied to strengthen digital defense systems.
Why AI and Cybersecurity Are a Perfect Match
AI and cybersecurity form a natural partnership. Cyber attackers constantly develop new strategies, making it impossible for static systems to keep up. AI brings dynamic intelligence — learning from data, identifying unusual patterns, and predicting future threats. Machine learning models can detect anomalies in real time, filter malicious emails, and even recognize subtle signs of data breaches that human analysts might miss.
The combination of AI’s predictive capabilities and cybersecurity’s defensive framework creates a proactive shield that evolves with the threat landscape. This synergy is what the course aims to teach — not just how AI works, but how it revolutionizes modern cyber defense.
Course Overview
The AI for Cybersecurity course is designed for learners with a basic understanding of computer science and an interest in how AI reshapes digital security. It spans four modules that balance theoretical knowledge with practical applications. The curriculum introduces AI and ML fundamentals, explores real-world cybersecurity scenarios, and concludes with ethical and regulatory discussions — giving learners a well-rounded understanding of the field.
Module 1 — Introduction to AI and Cybersecurity
The first module lays the foundation by explaining the core concepts of Artificial Intelligence and its various branches, such as supervised and unsupervised learning. It then transitions into the world of cybersecurity — covering the types of cyber threats, attack surfaces, and defense mechanisms. This module helps learners understand how AI fits into the broader landscape of security operations, from intrusion detection to vulnerability management.
Module 2 — AI Techniques for Cybersecurity
This module dives into the technical aspects of applying machine learning in cybersecurity. Learners explore how algorithms like decision trees, random forests, and deep neural networks can detect malware, phishing attempts, and network intrusions. It also introduces Natural Language Processing (NLP) and its use in analyzing threat reports, detecting fake news, and filtering spam emails. This section provides hands-on exposure to training and evaluating AI models for specific security tasks.
Module 3 — Real-World Use Cases
Theory comes to life in the third module, which presents practical applications of AI in cybersecurity. Case studies include identifying malicious web links, detecting domain generation algorithms (DGAs), and combating fake news or clickbait. Learners examine how AI-driven systems extract meaningful patterns from URLs, social media posts, and network traffic to identify and neutralize potential threats before they cause harm.
Module 4 — Ethics, Regulation, and the Future
The final module addresses one of the most critical aspects of modern technology — ethics and regulation. As AI takes on a bigger role in cybersecurity, issues such as data privacy, fairness, accountability, and transparency become vital. The course discusses global regulations like the EU AI Act and cybersecurity resilience frameworks that ensure responsible and ethical AI use. This section helps learners understand not only the technological aspects but also the societal and legal responsibilities tied to AI deployment.
Who Should Take This Course
The course is ideal for IT professionals, cybersecurity analysts, and data scientists who want to deepen their understanding of how AI enhances digital defense systems. It’s also suitable for students and tech enthusiasts with a foundational knowledge of computer science who wish to specialize in one of the fastest-growing technology intersections — AI and cybersecurity.
Skills You’ll Gain
By the end of the course, learners will have developed practical skills in:
-
Anomaly detection and intrusion prevention
-
Machine learning and deep learning applications
-
Natural Language Processing for security
-
Threat and malware classification
-
Ethical and regulatory considerations in AI
These skills can open pathways to advanced roles in cyber defense, threat analysis, and AI-driven security development.
Ethical and Future Implications
As powerful as AI is, it also raises questions about control, transparency, and bias. The course encourages reflection on these issues, highlighting the importance of responsible innovation. Learners are reminded that technology should always serve humanity — ensuring security without compromising ethical integrity or personal privacy.
Join Free: AI for Cybersecurity
Conclusion
AI for Cybersecurity is more than just an online course — it’s a gateway to understanding how intelligent machines are redefining the fight against cybercrime. By blending AI’s analytical strength with cybersecurity’s protective mission, this course empowers learners to think critically and act strategically in the digital age.
Whether you’re a budding security analyst, a data scientist, or an AI enthusiast, this program equips you with the tools and mindset needed to protect tomorrow’s connected world.
Master Git and GitHub with These 3 Must-Take Courses
Python Coding October 20, 2025 Git No comments
Are you ready to level up your coding workflow and collaborate like a pro? Whether you’re a beginner or looking to sharpen your version control skills, Git and GitHub are essential tools every developer must master. Luckily, CLCODING has three incredible courses to get you there—fast and effectively.
1. Learn Git and GitHub in One Day
⏱ Time-efficient, hands-on, and beginner-friendly
If you’ve been putting off learning Git because it seems too complicated, this course is perfect. In just one day, you’ll learn all the essential commands, understand how GitHub works, and even build a professional portfolio with your projects. It’s a crash course that actually works!
Why take this course?
-
Master Git basics and commands in a single day
-
Learn to track changes and manage versions effortlessly
-
Push your projects to GitHub like a pro
2. Introduction to Git and GitHub
📚 Step-by-step foundation for beginners
If you are completely new to version control, this course will gently guide you through the concepts of Git and GitHub. Understand how Git tracks changes, why branches are important, and how to collaborate with others on GitHub.
What you’ll gain:
-
Clear understanding of Git workflows
-
Ability to create and manage repositories
-
Confidence to contribute to open-source projects
3. Getting Started with Git and GitHub
🚀 Practical, project-oriented approach
This course is designed for those who prefer learning by doing. You’ll get hands-on practice creating repositories, making commits, and collaborating with team members. By the end, you’ll feel comfortable managing your own projects and contributing to others’.
Highlights:
-
Learn through real-world examples
-
Explore GitHub collaboration tools
-
Build a strong foundation for advanced Git techniques
💡 Pro Tip: Don’t just watch—practice! Open a GitHub account and start experimenting with your own projects as you go through these courses. By combining knowledge from all three, you’ll go from Git newbie to confident collaborator in no time.
Ready to take control of your code? Start learning Git and GitHub today and see the difference it makes in your workflow!
Learn Git and GitHub in One Day
Python Coding October 20, 2025 Git No comments
In the fast-paced world of software development, mastering version control is essential. Git and GitHub have become industry standards, empowering developers to manage projects efficiently, collaborate seamlessly, and maintain a professional workflow. If you want to level up your development skills, the “Learn Git and GitHub in One Day” course is the perfect starting point.
Why Git and GitHub Matter
Git is a powerful version control system that allows you to track changes in your code, revert to previous versions, and work on multiple features simultaneously without losing progress. GitHub, on the other hand, is an online platform that hosts your Git repositories, making collaboration with other developers effortless. Together, they form the backbone of modern software development.
What You’ll Learn in This Course
This course is designed to take you from zero to confident in a single day. Here’s what you can expect:
-
Git Basics – Learn how to initialize a repository, stage and commit changes, and understand the Git workflow.
-
Branching and Merging – Explore how to work on new features safely and merge them back into your main project.
-
GitHub Essentials – Push your projects online, manage repositories, and understand pull requests.
-
Collaborative Development – Learn how to contribute to open-source projects and work in teams.
-
Portfolio Building – Showcase your projects professionally, making you more attractive to employers.
Who Is This Course For?
Whether you’re a beginner programmer, a student, or a professional looking to strengthen your portfolio, this course is tailored for anyone who wants to understand Git and GitHub quickly and efficiently.
Key Takeaways
-
Gain hands-on experience with Git commands and workflows.
-
Learn to collaborate with others on GitHub projects.
-
Build a professional portfolio to demonstrate your skills.
-
Save time and reduce errors in your coding projects.
Final Thoughts
Mastering Git and GitHub doesn’t have to be overwhelming. With the right guidance, you can learn the essentials in just one day and start managing your projects like a pro. Take the first step toward better project management, smoother collaboration, and a standout portfolio.
Join Now: Learn Git and GitHub in One Day
Popular Posts
-
1. The Kaggle Book: Master Data Science Competitions with Machine Learning, GenAI, and LLMs This book is a hands-on guide for anyone who w...
-
Want to use Google Gemini Advanced AI — the powerful AI tool for writing, coding, research, and more — absolutely free for 12 months ? If y...
-
Every data scientist, analyst, and business intelligence professional needs one foundational skill above almost all others: the ability to...
-
Are you looking to kickstart your Data Science journey with Python ? Look no further! The Python for Data Science course by Cognitive C...
-
📘 Introduction If you’re passionate about learning Python — one of the most powerful programming languages — you don’t need to spend a f...
-
Explanation: 🔹 Import NumPy Library import numpy as np This line imports the NumPy library and assigns it the alias np for easy use. 🔹 C...
-
Code Explanation: 1. Defining the Class class Action: A class named Action is defined. This class will later behave like a function. 2. Def...
-
🔍 Overview If you’ve ever searched for a rigorous and mathematically grounded introduction to data science and machine learning , then t...
-
Code Explanation: 1. Defining the Class class Engine: A class named Engine is defined. 2. Defining the Method start def start(self): ...
-
Learning Data Science doesn’t have to be expensive. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced analyst, some of the best books in Data Sc...

.png)
.png)



.jpg)



.png)
.png)









.PNG)
.png)











.png)




.jpg)







.PNG)











