Introduction
In a world where being able to build software quickly and solve real-world problems is highly valued, simply knowing programming syntax isn’t enough. What really sets someone apart is the ability to apply skills in meaningful projects—whether it’s web apps, automation tools, data solutions or AI-driven agents. The course The Python Mega Course: Build 20 Real-World Apps and AI Agents is designed exactly for that: it goes beyond theory and guides you through building 20 distinct applications using Python, including AI agents, from scratch. If you are looking to move from “I know Python” to “I build useful things with Python”, this course could be a strong fit.
Why This Course Matters
There are countless Python courses that teach you syntax, control flow, data structures and maybe small examples. But many learners get stuck at “hello world” or “basic script” level. This course shifts the emphasis to application and breadth: you don’t just learn Python, you use Python to create real applications that mirror what you might encounter in a job or startup environment. By the end, you’re not just more knowledgeable—you’re more capable. This kind of hands-on, project-centric learning helps close the gap between learning and doing.
What You Will Learn – Course Highlights
Here’s a breakdown of what the course covers and what you’ll walk away with:
1. Comprehensive Application Building
You’ll build 20 real-world applications, each one focusing on a different domain or level of complexity. That could include automation scripts, web applications, data processing tools, GUI desktop apps, web scraping, and AI agents. The variety helps you see how Python applies across different problem sets and gives you a broad portfolio of work.
2. From Beginner to Pro in Python
The course is structured to take you from the basics—installing Python, writing your first scripts, understanding data types and control flow—through to advanced applications. As you progress, you’ll pick up modules, frameworks, libraries and best practices that let you build more professional systems.
3. Integrating Modern Tools and Libraries
Modern Python development isn’t just “write a script”. The course introduces you to libraries and frameworks used in real development: for example web frameworks (Flask, Django), GUI libraries (PyQt, etc.), automation tools (Selenium, etc.), data manipulation with Pandas, and even AI/agent frameworks (e.g., LangChain or other agent-oriented libraries). These give you exposure to the tools used in production settings.
4. Building AI Agents and Intelligent Applications
A standout component is the AI-agent building segment. You’ll learn how to design systems that leverage Python + modern AI/agent frameworks: agents that act, reason, interact, perhaps orchestrate tasks, integrate APIs and make decisions. This covers one of the most sought-after skill sets in 2025: building intelligent applications, not just static ones.
5. Hands-On, Project-First Learning
Rather than long lectures of theory, the course emphasizes doing. You build, you run, you debug, you iterate. By completing apps, you not only learn concepts—you internalize them. This accelerates your readiness to tackle your own side projects or job assignments.
Who Should Take This Course
-
Absolute beginners: If you’ve never programmed before but are motivated to build apps and make things happen, this course will take you from zero to building real applications.
-
Python developers with some experience: If you know the basics of Python but haven’t built many full-scale applications, this course will deepen your ability to create production-style apps and use libraries/frameworks.
-
Aspiring automation or AI engineers: If you want to learn how Python is used in automation, AI agents or glue-code to tie systems together, you’ll find relevant content here.
-
Side-project builders and hobbyists: If you like building things (automation tools, web apps, scrapings, agents) for your own use or for fun, the course gives you templates and guidance to make that happen.
If you’re already an advanced software engineer working on large distributed systems or specialized ML research, parts of this might feel basic—but you could still benefit from the breadth and application angle.
What You’ll Walk Away With
After finishing the course you will likely be able to:
-
Use Python confidently for building applications, not just scripts.
-
Understand and use a variety of libraries and frameworks (web, GUI, automation, data, agents).
-
Build several complete applications to showcase in your portfolio (20 is a large number).
-
Design, implement and deploy an AI agent or intelligent application using Python.
-
Be prepared to take on freelance projects, personal side-apps, or further move into data science, web development or AI systems.
Tips to Get the Most Out of It
-
Follow the projects fully: Build each app, run it, modify it. Don’t skip exercises—the value comes from building.
-
Extend the projects: After completing the guideline version, add new features or change behaviour. That helps go beyond what’s taught and makes the learning “yours”.
-
Use your own ideas: Once you’ve built several apps, think of your own app idea and apply what you learnt to it. That consolidates learning and gives you something unique to show.
-
Reflect on architecture: When building apps and agents, think about how you’d maintain, scale or deploy them—this mindset helps your work align with real-world expectations.
-
Document your work: Push your code to GitHub, write a short README for each project, maybe include screenshots or videos of them running. A portfolio of 20 projects plus descriptions stands out.
Join Free: Python Mega Course: Build 20 Real-World Apps and AI Agents
Final Thoughts
The Python Mega Course: Build 20 Real-World Apps and AI Agents is a powerful resource for anyone looking to go from “learning Python” to “building with Python”. Its project-based, application-focused structure helps you build skills that matter in practice. If you are ready to commit (coding takes time and effort), you’ll finish with not just know-how—but output: real apps, intelligent agents, and a portfolio that proves you can make things work. For anyone wanting to write Python and build meaningful software, this course is a very strong choice.





.png)
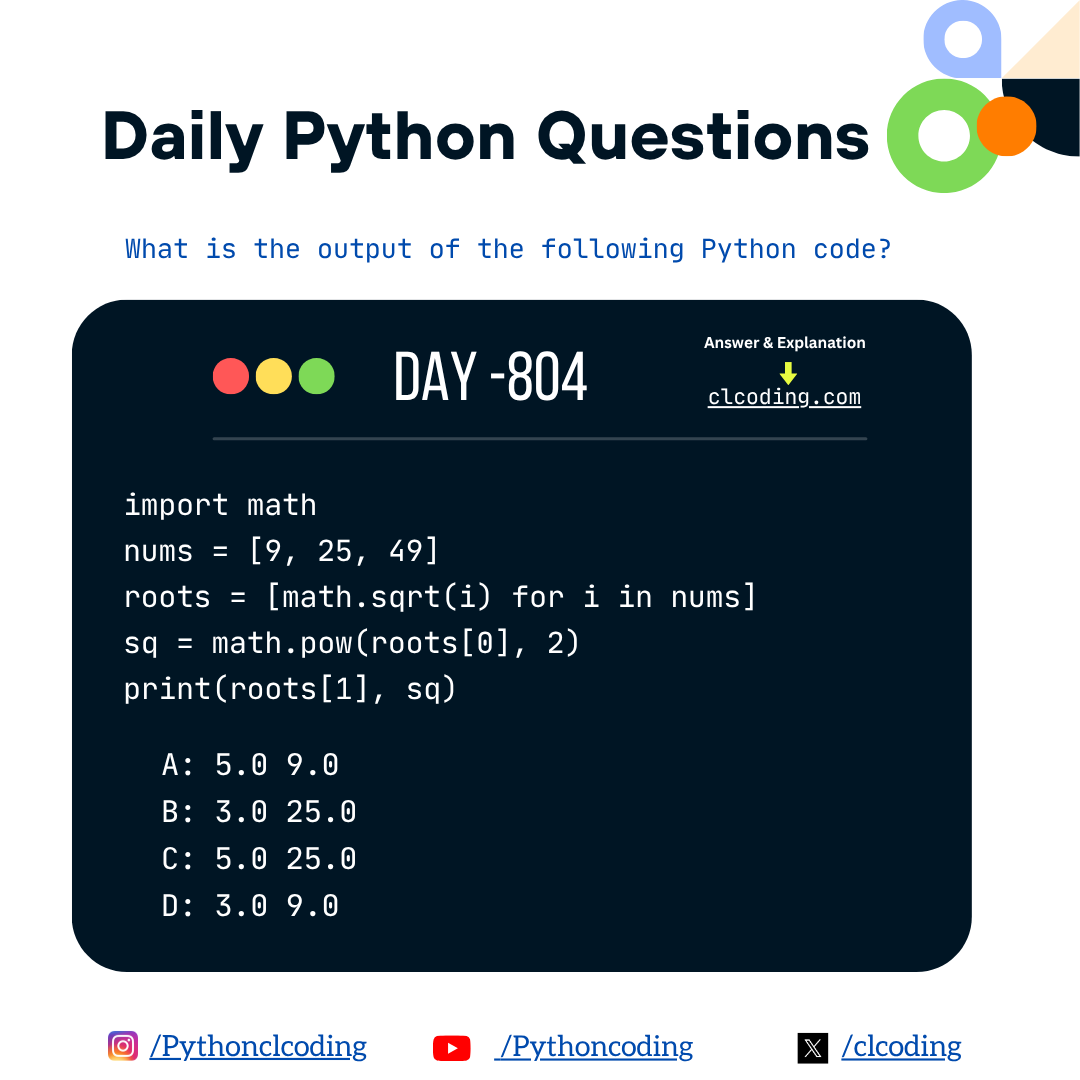.png)



.jpg)



.png)
.png)



.png)













.png)




.jpg)


%20by%20Allen%20B.%20Downey.jpg)


















