Code Explantion:
1. Importing Required Modules
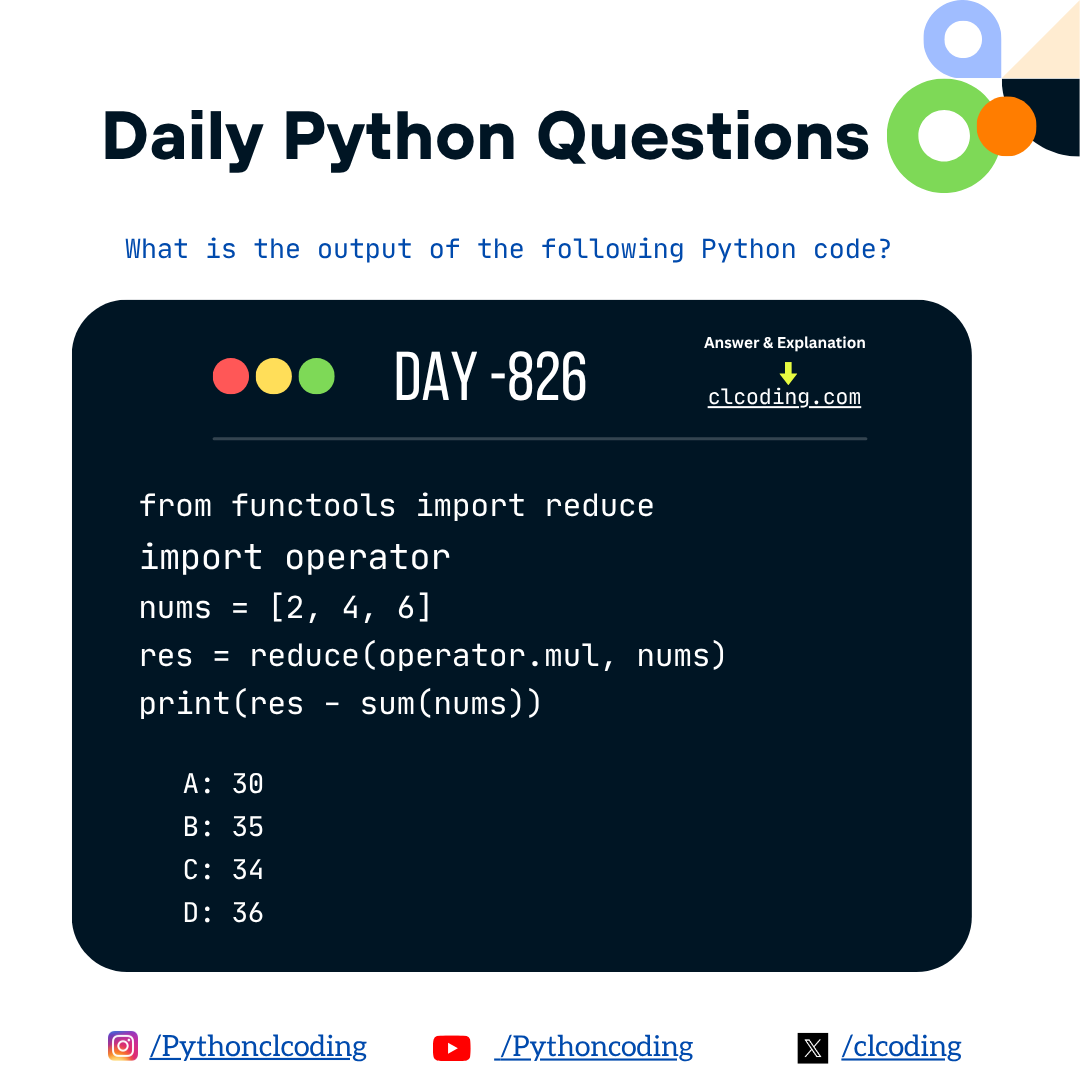
from functools import reduce
import operator
functools.reduce()
→ A higher-order function that applies a given function cumulatively to the items of a sequence, reducing it to a single value.
Example: reduce(func, [a, b, c]) → func(func(a, b), c)
operator
→ Provides function forms of built-in operators like addition (operator.add), multiplication (operator.mul), etc.
2. Defining the List of Numbers
nums = [2, 4, 6]
Creates a list nums containing three integers: 2, 4, 6.
This will be used as the input for our reduce() function.
Output (conceptual):
nums = [2, 4, 6]
3. Using reduce() to Multiply All Elements
res = reduce(operator.mul, nums)
Let’s understand this step-by-step:
operator.mul → multiplies two numbers (same as using *).
reduce(operator.mul, nums) → performs:
((2 * 4) * 6)
Step-by-step calculation:
First operation → 2 * 4 = 8
Next operation → 8 * 6 = 48
So,
res = 48
Output (conceptual):
res = 48
4. Subtracting the Sum of the List
print(res - sum(nums))
Let’s compute it:
Expression Value
sum(nums) 2 + 4 + 6 = 12
res 48
res - sum(nums) 48 - 12 = 36
Printed Output:
36

.png)

.png)






%20by%20Allen%20B.%20Downey.jpg)







.png)




.jpg)
%20by%20Allen%20B.%20Downey.jpg)



















0 Comments:
Post a Comment